A guide to Mutual Funds in Nepal
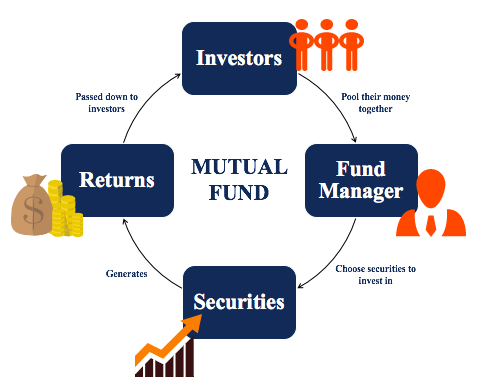
Mutual funds have emerged as a popular investment vehicle in Nepal, offering individuals a means to pool their resources and invest in a diversified portfolio managed by professionals. These funds play a significant role in the country's financial market, providing opportunities for both novice and experienced investors. In this blog, we will explore mutual funds in Nepal, delving into their regulatory framework, types and interaction with the Nepal Stock Exchange (NEPSE).
Regulatory framework and overview
In Nepal, mutual funds are regulated by the Securities Board of Nepal (SEBON), which ensures that these funds operate within a defined legal structure to protect investors' interests. The Mutual Fund Regulation, 2067 (2010) serves as the cornerstone of the regulatory framework, outlining the formation, registration, management, and operational guidelines for mutual funds.
Currently, there are 43 mutual funds operating in Nepal, out of which 36 are closed-end and 7 are open-end.
Types of Mutual Funds in Nepal
Mutual funds in Nepal can be broadly categorized into two types:
Closed-ended funds: These funds have a fixed number of units and are listed on the Nepal Stock Exchange (NEPSE). Investors can trade these units in the secondary market, and the market price may vary from the Net Asset Value (NAV) depending on demand and supply dynamics.
Open-ended funds: Unlike closed-end funds, open-end funds do not have a fixed number of units. Investors can buy or redeem units directly from the fund at the NAV. These funds are not listed on NEPSE, and transactions are managed directly by the fund managers.
Mutual Funds and NEPSE: A symbiotic relationship
The Nepal Stock Exchange (NEPSE) plays a critical role in the functioning of mutual funds, especially closed-end funds, which are traded on the exchange. Here’s how NEPSE interacts with mutual funds:
Listing and trading: Closed-end mutual funds are listed on NEPSE, providing liquidity to investors. These units can be bought and sold like stocks, with their market prices determined by supply and demand.
Market price vs. NAV: The market price of mutual fund units on NEPSE can differ from the NAV. Units may trade at a premium (above NAV) or a discount (below NAV) based on market sentiment, fund performance, and investor expectations.
Impact of NEPSE index: Since many mutual funds invest heavily in equities, their performance is often correlated with the overall NEPSE index. A bullish NEPSE index typically leads to higher NAVs and potentially higher market prices for mutual fund units.
Performance metrics and investment strategies
Investors in mutual funds should be aware of key performance metrics:
Net Asset Value (NAV): This is the per-unit value of the fund, reflecting its overall performance. It is calculated by dividing the total value of the fund's assets by the number of outstanding units.
Price to NAV Ratio: On NEPSE, the price of mutual fund units relative to their NAV indicates whether they are trading at a premium or discount. This ratio is crucial for making informed trading decisions.
Investment strategies: Mutual funds in Nepal typically follow various strategies, including equity-oriented funds, fixed-income funds, and balanced funds, offering a mix of risk and return options to investors.
Image source: Corporate Finance Institute